
Of the many factors influencing the epidemiology of acute aseptic meningitis syndrome or viral encephalitis, the most important for determining the cause are the patient's age, immunocompetence, geographic location, and the season. Less common causes of encephalitis are the herpes viruses (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, varicella-zoster virus ), measles, and rabies ( Table 64-1). Enteroviruses and arboviruses are most often the agents in epidemics, whereas HSV-1 is the most common cause of sporadic cases of encephalitis in the United States.
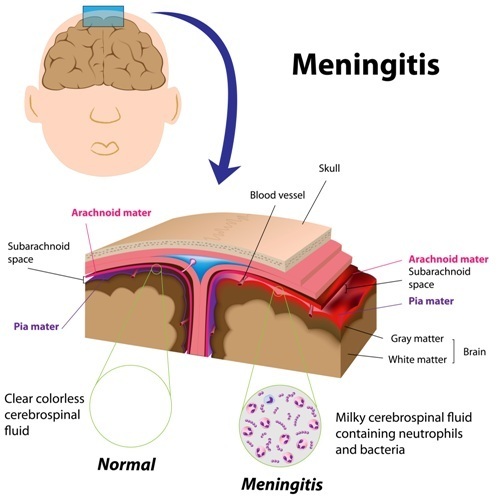
Viral meningitis or encephalitis can occur either sporadically or epidemically. Recruitment of blood monocytes into the CSF may result from the effects of chemokines such as macrophage inflammatory protein-α (MIP-α), RANTES, IL-8, and growth related oncogene-α (GRO-α). These cytokines are thought to be produced locally in the brain. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) are present in the CSF of patients with viral meningitis and may have an anti-inflammatory effect. Proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels are high in the CSF of patients with viral meningitis but not in patients with bacterial meningitis. In viral meningitis, activated T cells and monocytes are found in the CSF. The extent of the neuronal damage may contribute to the clinical severity of viral meningoencephalitis. With viral replication in neural cells, cell death or dysfunction results. In these cases, the virus may infect the brain by retrograde travel along axons in the spinal cord or the brain. Nonhematogenous routes of transmission also exist these routes may be important in the pathogenesis of rabies or adult-onset herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE). Viruses may invade the CNS through the choroid plexus or by direct penetration of the endothelium of cerebral blood vessels. Most viruses reach the CNS by the hematogenous route. Clin Infect Dis 2008 47:303-327.Entry and replication of the viruses that cause meningitis and encephalitis occur extraneurally. The management of encephalitis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice Guidelines for the Management of Bacterial Meningitis. Impact of in-hospital enteroviral polymerase chain reaction testing on the clinical management of children with meningitis. Comparison of antibiotic and acyclovir usage before and after the implementation of an on-site FilmArray meningitis/encephalitis panel in an academic tertiary pediatric hospital: a retrospective observational study.


Impact of the implementation of a rapid meningitis/encephalitis multiplex polymerase chain reaction panel on IV acyclovir duration: multicenter, retrospective cohort of adult and pediatric patients. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2018 37:868-71. Impact of cerebrospinal fluid multiplex assay on diagnosis and outcomes of central nervous system infections in children: a before and after cohort study. Diagnosis, Initial Management, and Prevention of Meningitis. Confederation of Meningitis Organisations Fact Sheet.The stated performance is the overall aggregate performance of the prospective clinical study data presented in the IFU.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
